Email format error
Email cannot be empty
Email already exists
6-20 characters(letters plus numbers only)
The password is inconsistent
Email format error
Email cannot be empty
Email does not exist
6-20 characters(letters plus numbers only)
The password is inconsistent

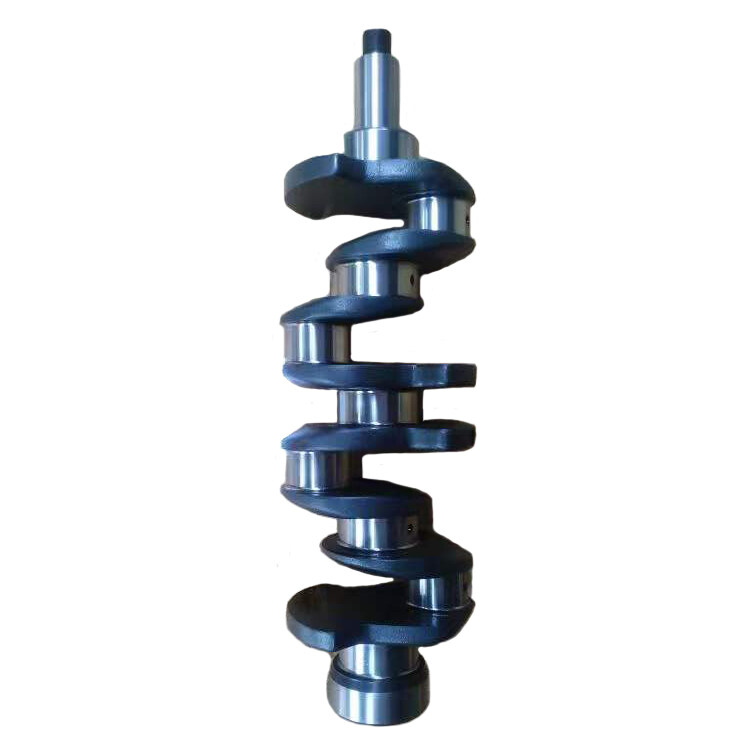
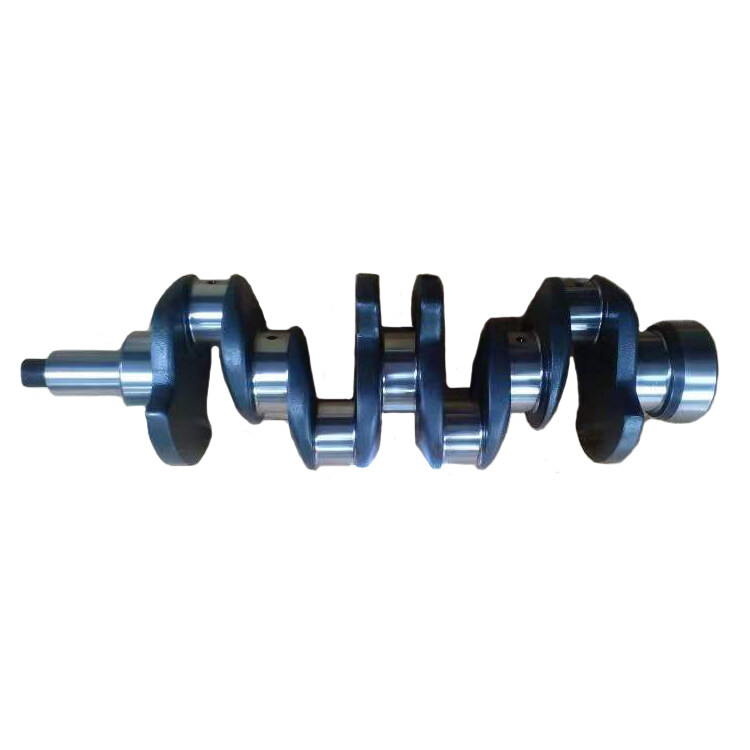
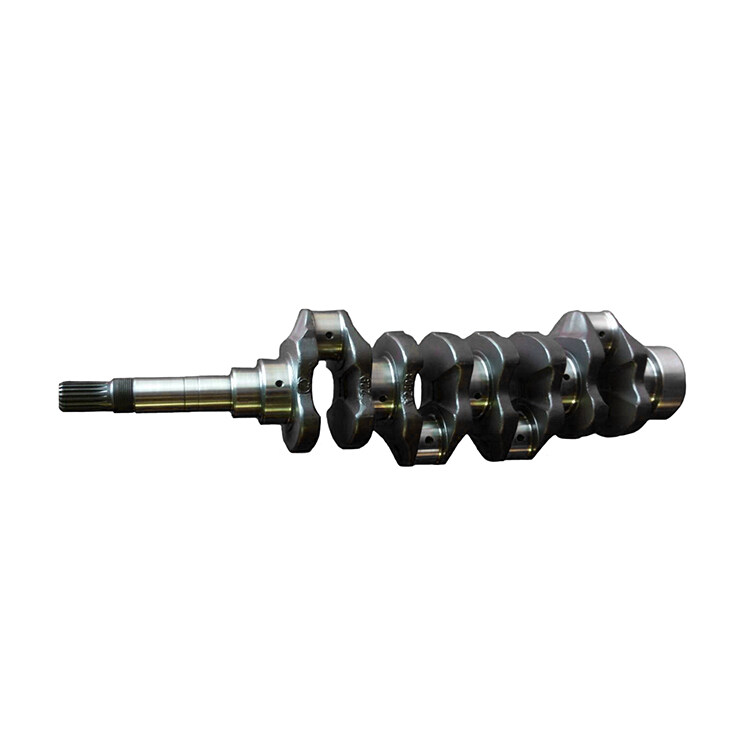
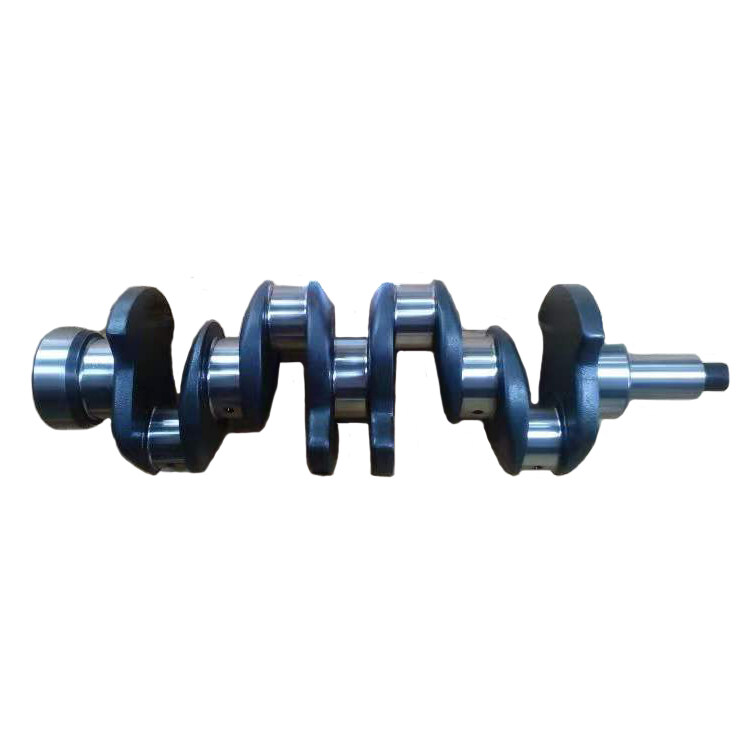
4BD1 Diesel Engine Crankshaft 5-12310-163-1 5123101631
The crankshaft is the central part of the engine. It takes the force from the connecting rod and converts it into torque that is output through the crank. It drives other important accessories on the engine by turning its flywheel.
The 4BD1 is a popular Isuzu diesel engine, and the crankshaft is a crucial component within the engine's assembly. The crankshaft in a diesel engine like the 4BD1 serves the fundamental purpose of converting the reciprocating motion of the pistons into rotary motion, which powers various applications such as trucks, industrial machinery, and generators. Here are key details about the 4BD1 Diesel Engine Crankshaft:
Function:
- The primary function of the crankshaft is to convert the linear (up-and-down) motion of the engine's pistons into rotary motion. This rotary motion is transmitted to the vehicle's wheels or the equipment's output shaft, providing mechanical power.
Construction:
- Crankshafts are typically made from high-strength materials, such as alloy steel, to withstand the mechanical forces, heat, and stress generated during engine operation.
Crankpins and Journals:
- The crankshaft features multiple crankpins and journals that are strategically placed and designed to connect to the engine's connecting rods and pistons. The crankpins provide the attachment points for the connecting rods.
Balancing:
- The design of the crankshaft includes counterweights and balancing to minimize vibrations and ensure smooth engine operation.
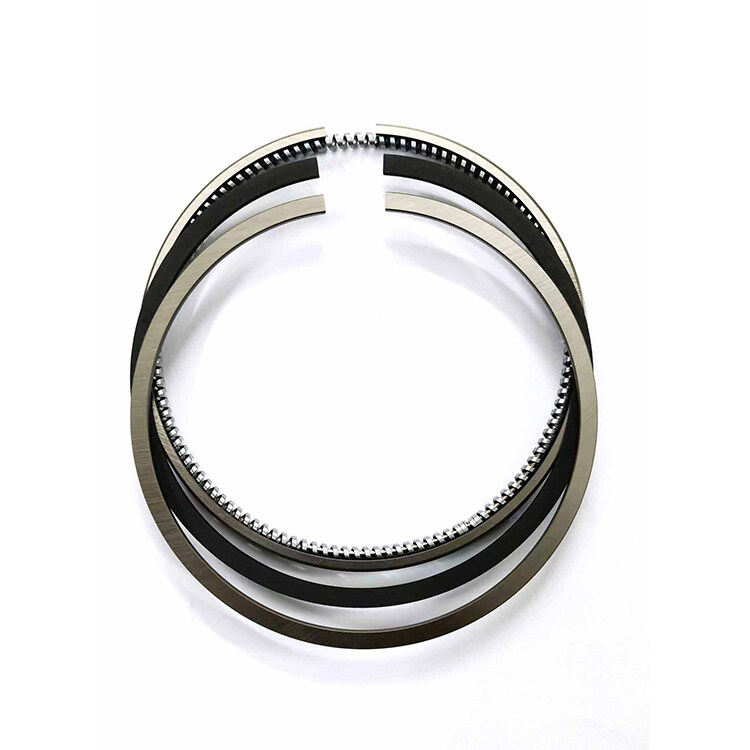
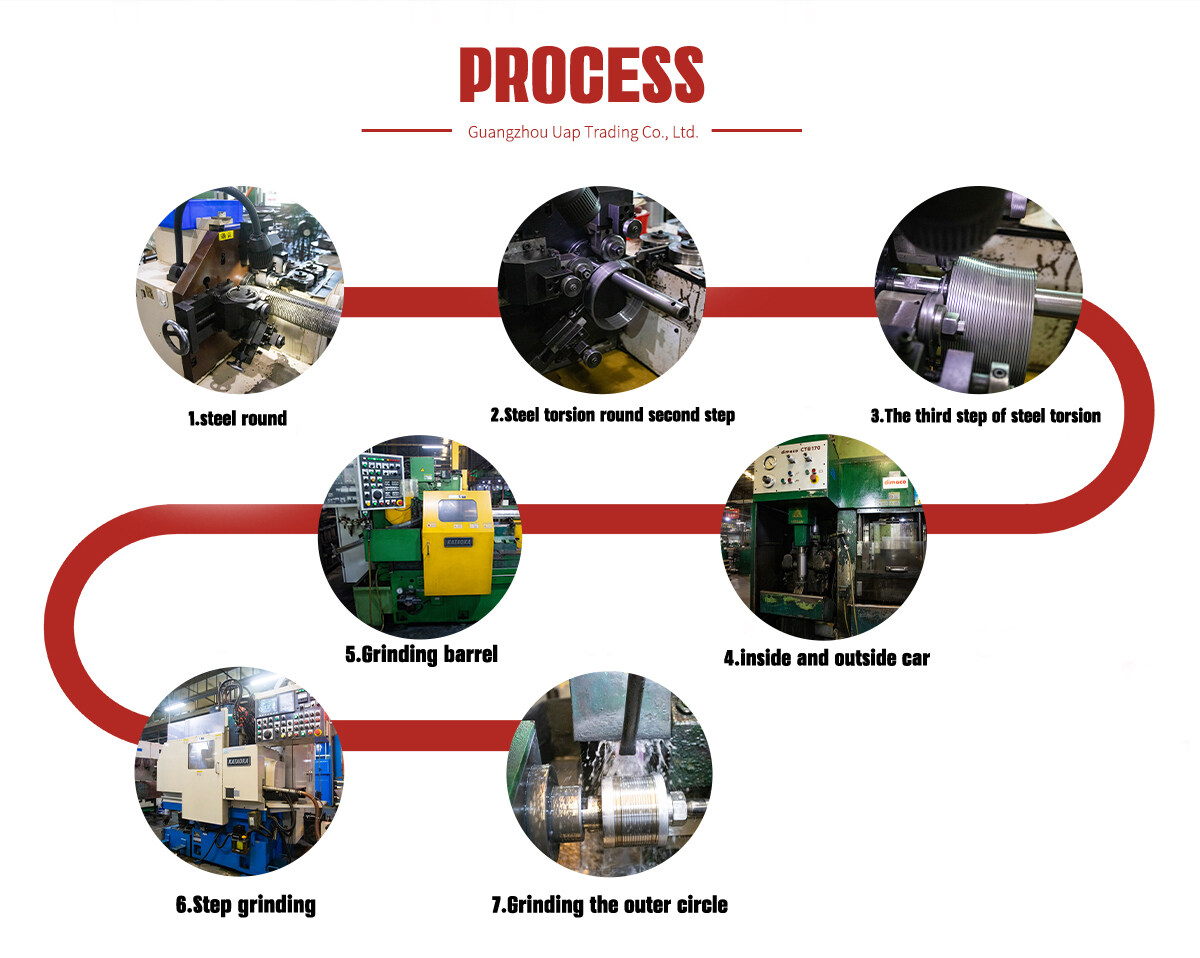
The crankshaft is a robust and reliable component that is made from high-strength alloy material. Its high-precision machining ensures optimal performance, while its exceptional wear resistance enables it to operate reliably in high-pressure and harsh working conditions. The crankshaft’s design is optimized for durability and longevity, making it a dependable and cost-effective solution for heavy-duty applications.
Wear-resistance and Corrosion-resistance:
The crankshaft is subjected to high-stress and high-temperature conditions during operation, which can cause significant wear and tear over time. However, the crankshaft is crafted from high-strength alloy material and undergoes high-precision machining to ensure optimal performance and durability. The material used in the crankshaft’s construction is highly resistant to wear and corrosion, which enables it to operate reliably in harsh working conditions. Additionally, the crankshaft’s design is optimized for durability and longevity, ensuring that it can withstand the rigors of heavy-duty applications.
High Level of Accuracy and Precision:
the crankshaft features a high level of precision and accuracy in its machining. This ensures that the crankshaft operates smoothly and efficiently, reducing the risk of vibration and other issues that can cause damage to the engine. The high-precision machining also helps to ensure that the crankshaft is perfectly balanced, which is essential for maintaining the engine’s performance and reducing wear and tear on other components.
Withstand High Pressure and Harsh Environment:
The crankshaft is designed to operate reliably in demanding environments, such as heavy-duty construction equipment, agricultural machinery, and marine vessels. Its high-strength alloy material and exceptional wear resistance enable it to withstand the stresses and strains of these applications, ensuring that the engine operates smoothly and efficiently. Additionally, the crankshaft’s design is optimized for durability and longevity, which reduces the need for frequent maintenance and repairs.
Product Parameter:
|
Product Name |
Engine Crankshaft |
|
Application |
Engineering Machinery Engine |
|
OEM Number |
5123101631 |
|
Engine Number |
4BD1 |
|
Year |
1980-2006 |
|
Material |
Alloy Steel |
|
Car Model |
ISUZU |
|
Size |
STD |
|
Condition |
New |
|
Warranty |
12 Months |
|
Packing |
Wooden Case |
|
Application Industries |
Machinery Repair Shops, Retail, Vehicles & Accessories |
The Precaution Of Engine Crankshaft?
- Please check carefully whether it is neat or has other damages;
- In installation, please use suitable tools and technology to ensure its right installation and whether it well match with other parts;
- In using, please regularly check it whether it needs to maintain or change.
What is an engine crankshaft?
The crankshaft is an important part of the engine. It takes the force from the connecting rod and converts it into torque that is output through the crankshaft and drives other accessories on the engine. The crankshaft is subjected to the combined effect of centrifugal force of rotating mass, cyclically varying gas inertia force, and reciprocating inertia force, which subjects the crankshaft to bending and torsional loads. Therefore, the crankshaft is required to have sufficient strength and stiffness, and the journal surface needs to be wear-resistant, work evenly, and have good balance.
To reduce the crankshaft mass and centrifugal force generated by the movement, the crankshaft journal is often made hollow. Each journal surface is opened with oil holes, to introduce or lead out the oil, used to lubricate the journal surface. To reduce stress concentration, the main journal, crank pin, and crank arm connections are used in the transition arc connection.
The role of the crankshaft balance weight (also known as a counterweight) is to balance the rotational centrifugal force and its moment, and sometimes also balance the reciprocating inertia force and its moment. When these forces and moments themselves are balanced, the counterweight can also be used to reduce the load on the main bearing. The number, size, and placement of the balance weight according to the engine cylinder number, cylinder arrangement, crankshaft shape, and other factors to consider.

Balance weight and crankshaft are generally cast or forged into one, high-power diesel engine balance weight and crankshaft separate manufacturing, and then bolted together.
The crankshaft is generally made of medium carbon steel or medium carbon alloy steel die forging. To improve the wear resistance and fatigue strength, the surface of the journal is quenched or nitrided by high frequency, and finely ground to achieve high surface hardness and surface roughness requirements. It cooperates with the connecting rod to change the gas pressure acting on the piston into rotating power, which is transmitted to the transmission mechanism of the chassis. At the same time, it drives the gas distribution mechanism and other auxiliary devices, such as fans, water pumps, generators, etc.
When working, the crankshaft is subjected to gas pressure, inertia force, and moment of inertia, and is subjected to large and complex forces, as well as the impact of alternating loads. At the same time, the crankshaft is a high-speed rotating part, therefore, the crankshaft is required to have sufficient stiffness and strength, good ability to withstand impact loads, wear resistance, and good lubrication.

Materials of automobile crankshaft
There are three main types of crankshaft materials.
One is a steel crankshaft, one is a ductile iron crankshaft, and the other is new aluminum alloy composite material.
Steel crankshaft is mainly the steel material that determines the main quality of the crankshaft, in addition to the processing technology and processing accuracy, steel crankshaft is generally used rounded corner rolling process. Crankshaft industry precision is not visible to the naked eye.
Ductile iron crankshaft in addition to the use of rounded corner rolling process, but also nitriding treatment, nitriding treatment of the crankshaft color ooze. General personnel to buy crankshafts recommended to buy the original engine manufacturers, basically to ensure quality. When selecting, just pay attention to the crankshaft part not to have trachoma, pull marks, etc. can be, which generally will not be a problem.
New aluminum alloy composite materials, since the 1990s, foreign countries have widely used high-strength aluminum alloy to replace traditional materials to achieve lightweight. It is reported that many companies have produced all-aluminum engines, whose crankshafts use pressure casting fiber and particle-reinforced aluminum alloy composites.
The application of fiber-reinforced and particle-reinforced composite technology in industrial mass production has not been reported, mainly because of the complicated production process of composite materials, which is currently only in laboratory single-piece small batch production.